en:substitute-goods-examples
Examples of Substitute Goods
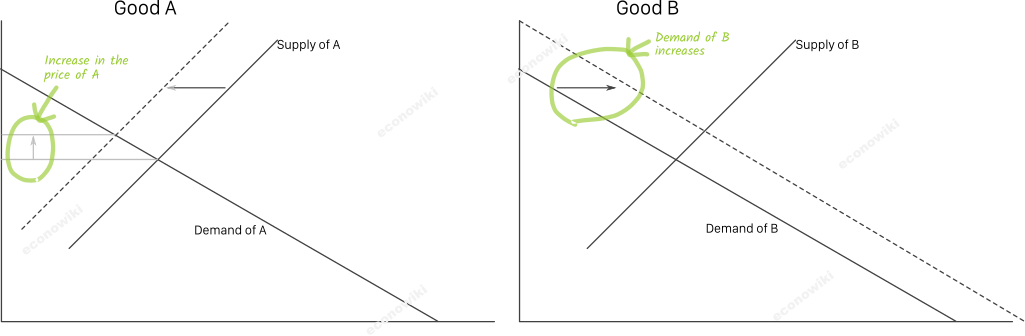
Substitute Goods are those goods that can be used to satisfy the same necessity. Substitute Goods have a positive cross elasticity of demand. That is, when the price of one good increases, the quantity demanded of the other good increases, because the user can substitute one good for another.
Complementary goods, in contrast, have a negative cross elasticity of demand.
Examples of substitute goods are (more than 10 examples):
- Tea and coffee
- Bus, taxi and car
- Bananas and Apples and Oranges
- Airplane and train
- Amazon Kindle books and paper books
- Butter and margarine
- Beer and Wine
- McDonald's and Burger King.
- Starbucks vs Dunkin'Donuts
- Starbucks Blonde Roast Coffee and Starbucks Medium Roast Coffee
- Bing Search and Google Search
- Electric cars and gas cars
- Private schools and public schools
- Coca Cola and Pepsi
Graphical Analysis of Substitute Goods:
en/substitute-goods-examples.txt · Last modified: 2018/09/29 11:37 by federico
Discussion